|
2008 SSI Report
|
The Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act
of 1996 (Public Law 104-193) directs the Commissioner of Social Security
to report annually to the President and to the Congress on the status of the
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) program. A required element of these reports is to
provide projections of program participation and costs through at least 25
years. This report is the twelfth of such reports, and following are its major highlights and findings.
Highlights of the SSI Program
• |
The SSI program is a nationwide Federal assistance
program administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA)
that guarantees a minimum level of income for needy aged, blind, or disabled individuals.
It acts as a safety net for individuals who have
little or no Social Security or other income and limited resources.
|
• |
In January 2008, 7.1 million individuals received monthly Federal SSI payments averaging $445,
up slightly from 7.0 million recipients with an average payment of $435 in January 2007.
|  [D]
[D]
|
• |
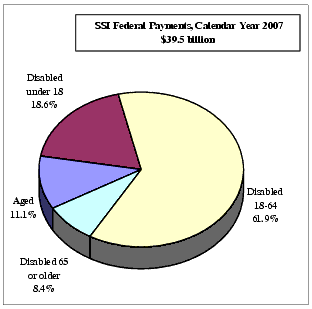
Federal expenditures for cash payments under the SSI program during calendar year 2007
increased 4.6 percent to $39.5 billion, while the funds made available to administer the SSI program
in fiscal year 2007 decreased 2.1 percent to $2.9 billion. In calendar year 2006 the
corresponding Federal program expenditures and cost of administering the SSI program were
$37.8 billion and $3.0 billion, respectively.
|
Major Findings of the Report
• |
By 2032, the end of the 25-year projection period, the Federal SSI recipient population is estimated to reach 9.5 million. The projected growth in the SSI program over the 25-year period is largely due to the overall growth in the U.S. population. The rate of participation is projected to vary somewhat by age group, with the overall participation rate of the 65 or older age groups projected to decline and the participation rate of the under 65 age groups projected to increase slightly.
|
• |
Expressed as a percentage of the total U.S. population, the number of Federal SSI recipients
increased slightly from 2.26 percent in 2006 to 2.28 percent in 2007, and is projected to
increase gradually to 2.53 percent of the population by 2032 due largely to the changing age
distribution of the population.
|
• |
Federal expenditures for SSI payments in calendar year 2008 are estimated to increase by
$2.3 billion to $41.8 billion, an increase of 5.7 percent from 2007 levels.
|
• |
In constant 2008 dollars, Federal expenditures for SSI payments are projected
to increase to $55.4 billion in 2032, a real increase of 1.2 percent per year.
|
• |
When compared to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Federal SSI expenditures are projected
to decline over time, from the current level of 0.29 percent of GDP in 2007 to 0.25 percent of GDP by 2032.
|
|